Building Blocks To Becoming a Pilot
The use of science, mathematics, and technology to solve problems.
Desire to understand how things work and solve puzzles; Strong analytical, computer, communication skills; Willingness and persistence to risk failure until a problem is resolved or improved.

Problem: Bulky and heavy materials impact lift |
Solution: Lightweight materials identified and tested |

Problem: As aircraft get faster and more maneuverable, stronger frames required |
Solution: Metal Structure, monocoque fuselage, development of light weight metals such as aluminum |

Problem: For passenger comfort and safety need to fly above weather |
Solution: Pressurized cabins (discovery of metal fatigue) |

Problem: Increased speeds generate heat and stress on conventional metals |
Solution: Advanced alloys and metals developed such as magnesium and titanium |

Problem: Lighter airframes needed for increased range and better fuel economy |
Solution: Composite structure, carbon fiber wings and fuselage |
Problem: Sustainability, reliability, carbon emissions |
Solution: Smart structure? Self-healing structure? Piezoelectric wing warping? |

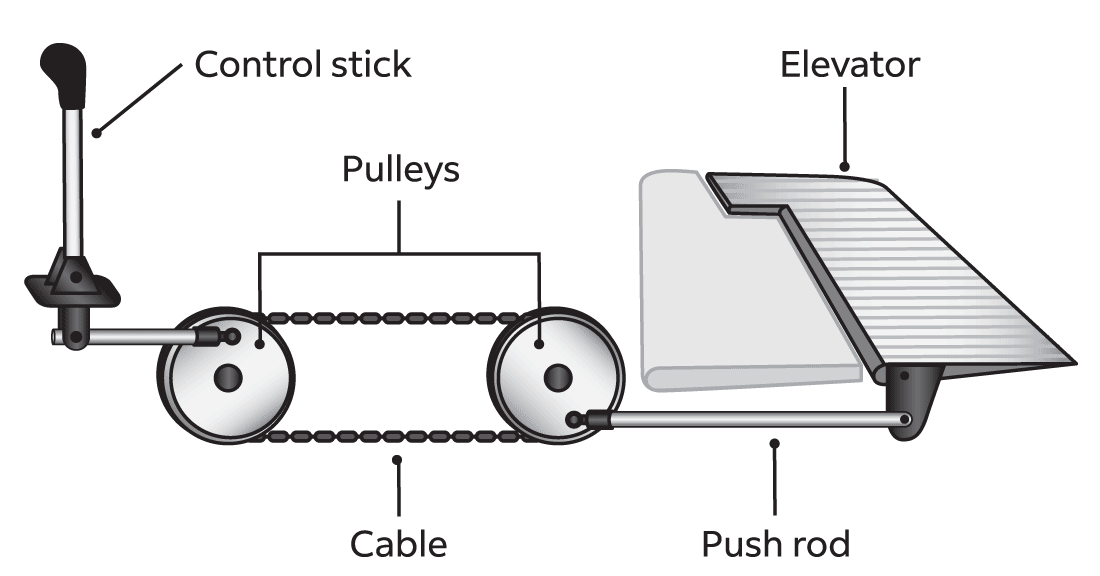
Mechanical control with pulleys, rods, and cables
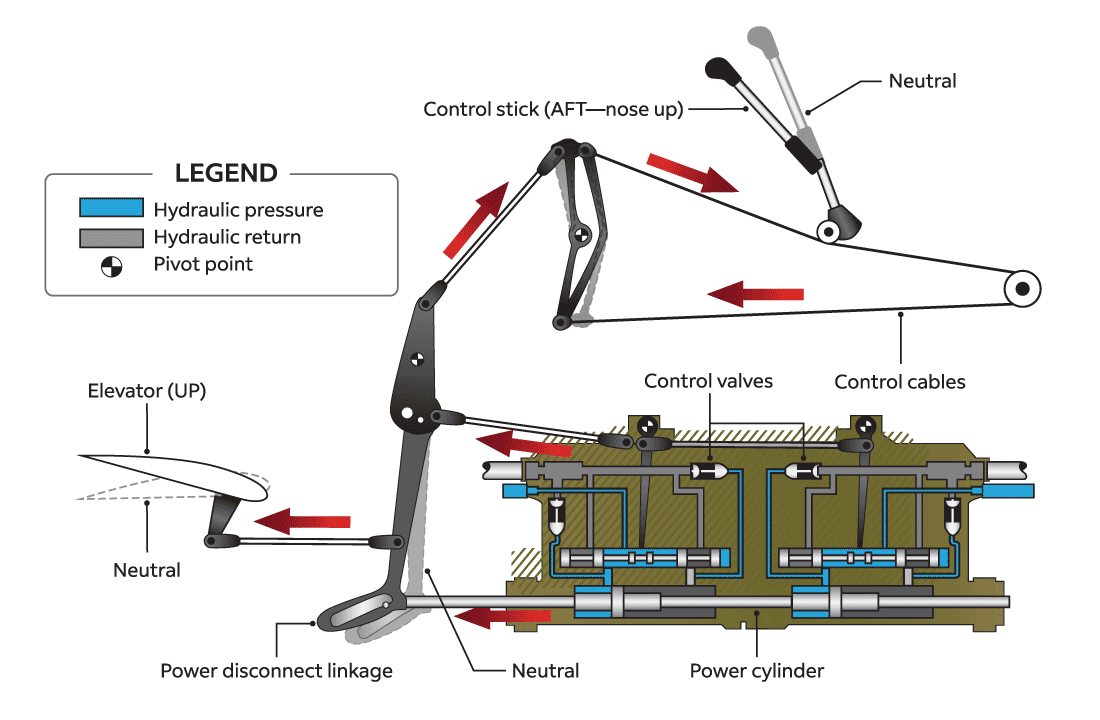
Problem: As speed and size increase more force is required by pilot to control aircraft |
Solution: Hydromechanical controls accept inputs from pilots and apply hydraulic force to controls surfaces |
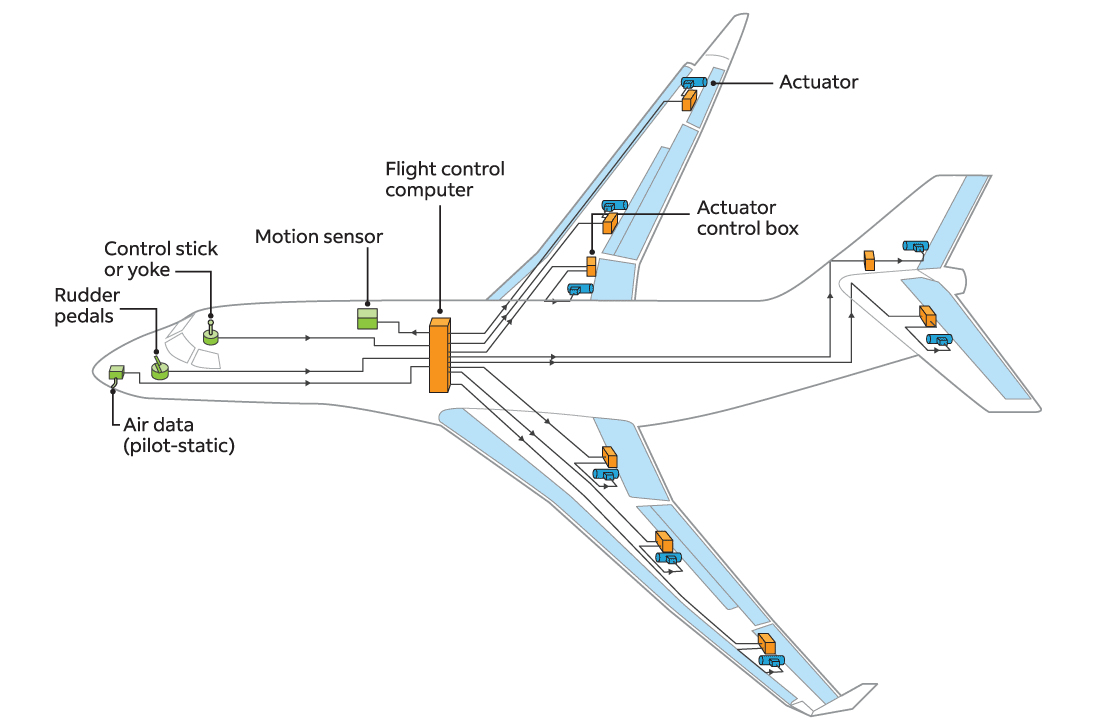
Problem: Increase safety, increase fuel efficiency, reduce weight, reduce maintenance |
Solution: Fly-By-Wire. Input from pilot goes to computer which provides quickest, safest, and most efficient flight control |
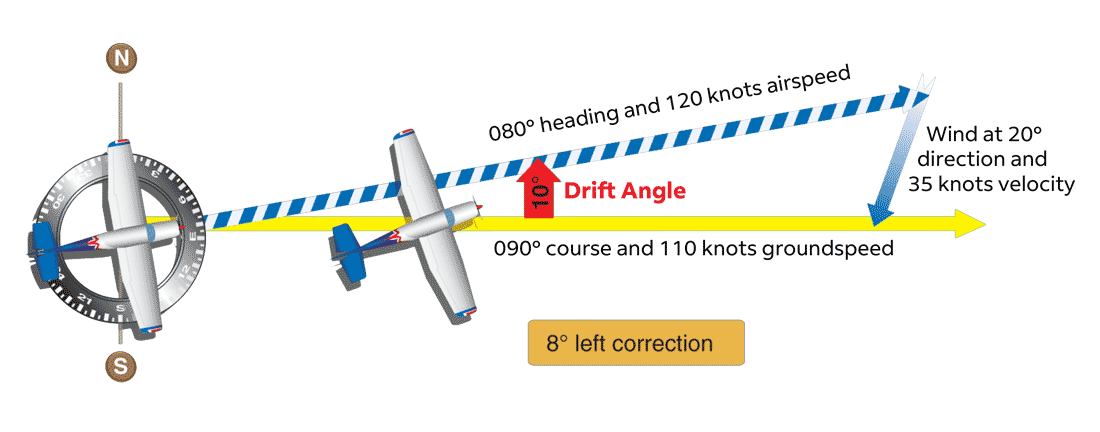
Dead-reckoning
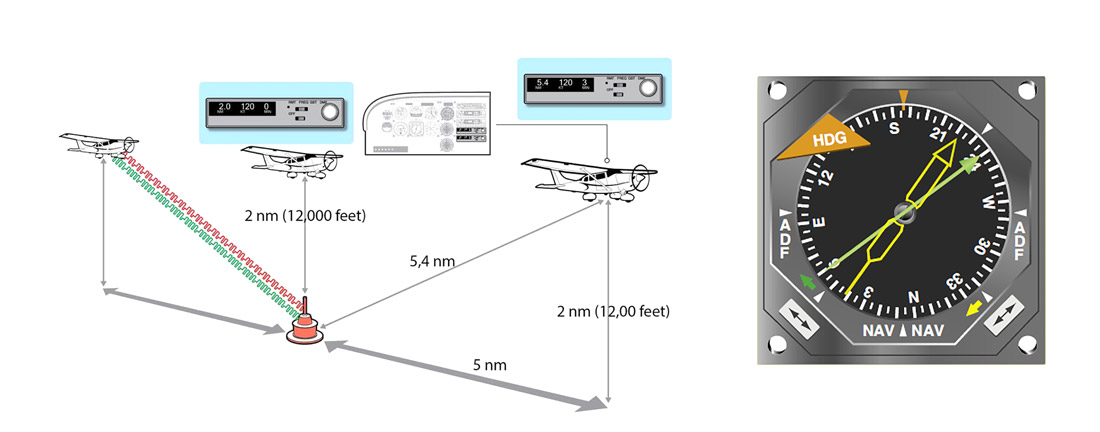
Problem: Inaccurate, requires clear weather |
Solution: Ground based radio beacons and onboard Radio Navigation equipment guide pilots from waypoint to waypoint |
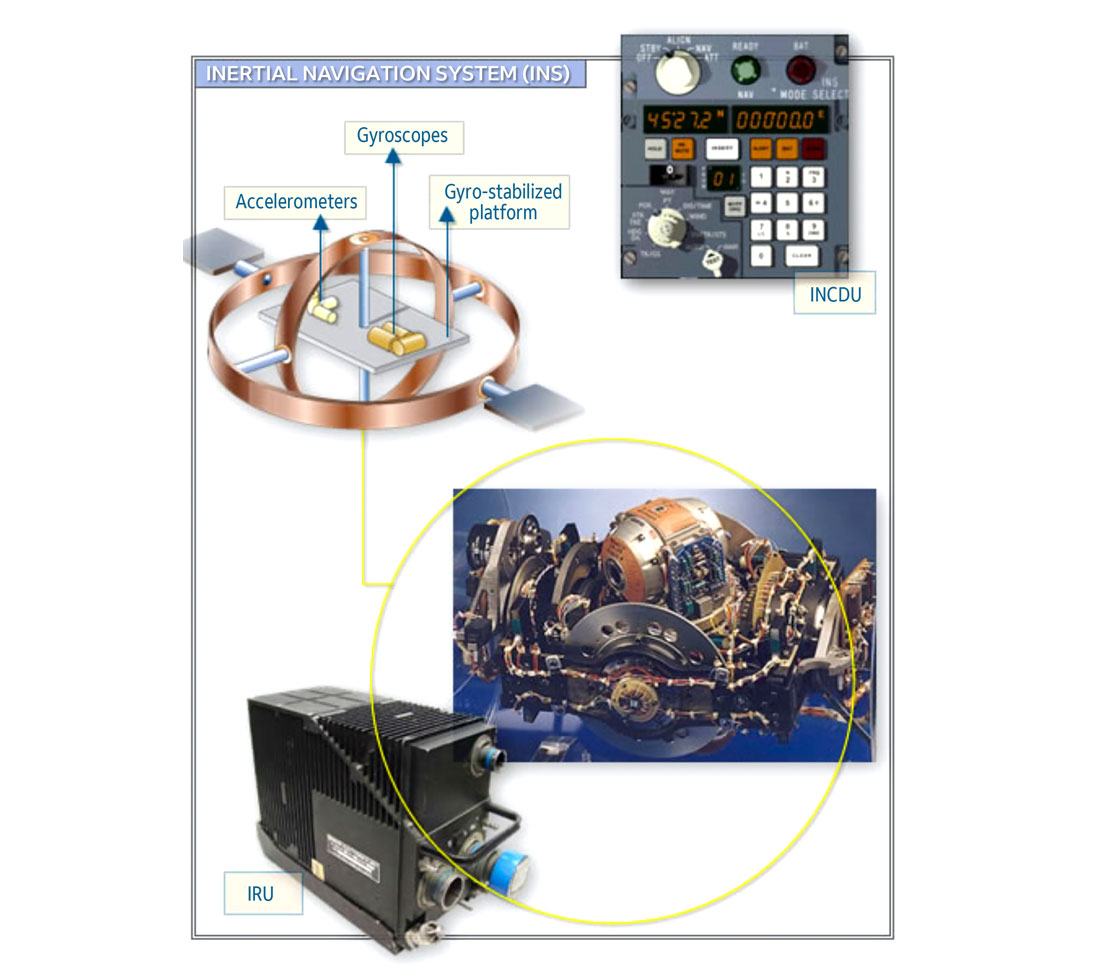
Problem: Limited range. Overseas and remote area navigation |
Solution: Inertial Navigation. Gyros, accelerometers and computers on aircraft determine heading and distance and navigate independently |
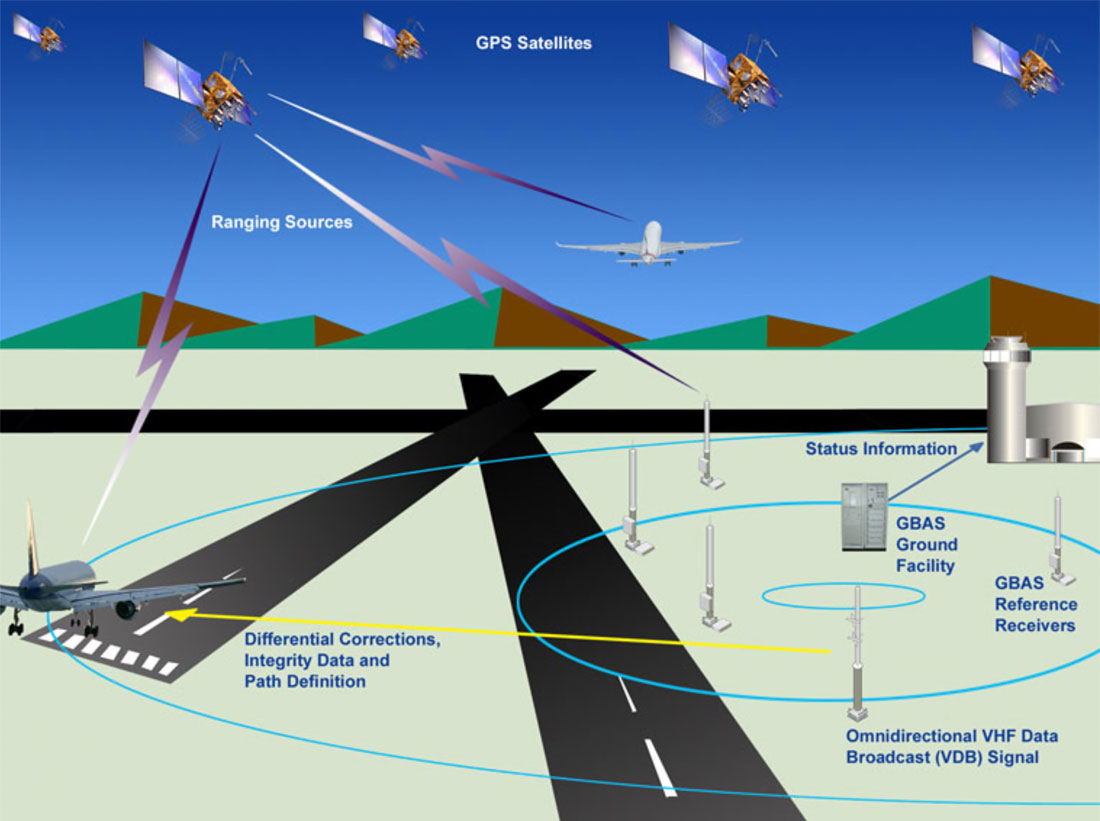
Problem: INS is prone to inaccuracy over time and expensive to maintain |
Solution: GPS Navigation. Space-based Global Positioning enables more coverage and greater accuracy |
Maintain, troubleshoot, and repair a fleet of over 400 aircraft, throughout the world
Desire to understand and solve maintenance issues with aircraft. Pride in work accomplishments. Ability to work as a team or individually. Strong analytical, computer, communication skills. Willingness and persistence to resolve problems and foresight for improvements.

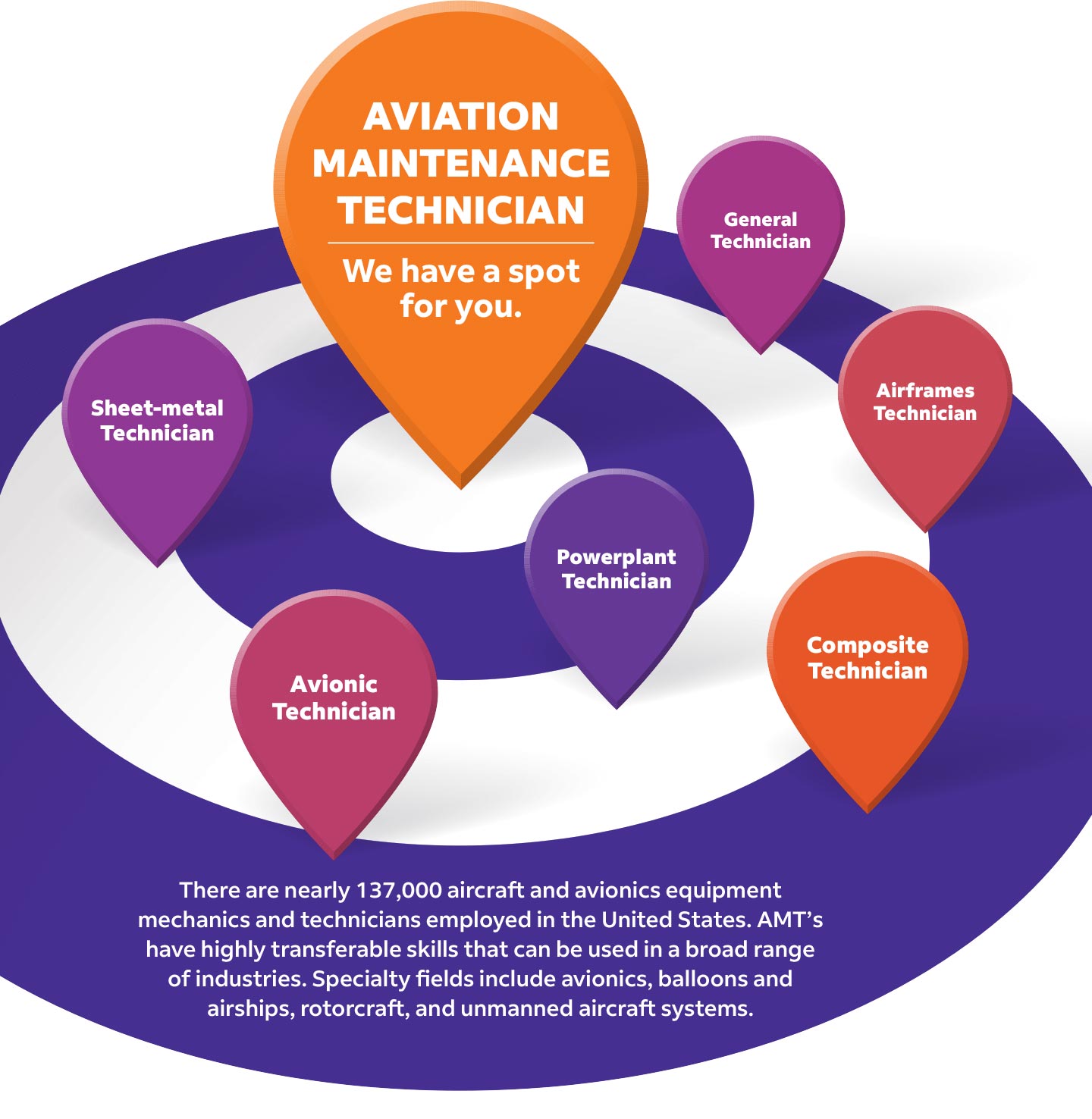
General Technician
Airframe and Powerplant (A & P) mechanics are certified generalist mechanics who can independently perform many maintenance and alteration tasks on the aircraft.
Sheet-metal Technician
A skilled tradesperson who specializes in fabricating, installing, and repairing metal products and structures on the aircraft.
Airframes Technician
Repairs and maintains most parts of an aircraft, including the landing gear, brakes, and air-conditioning system.
Composite Technician
Uses a wide range of products, such as carbon fiber, fiberglass, graphite, and Kevlar, to make various fabrication and repairs to include painting of aircraft.
Powerplant Technician
Repairs and maintains the engine and engine subsystems on the aircraft.
Avionic Technician
Repair and maintain a plane's electronic instruments, such as radio communication devices and equipment, radar systems, navigation aids, and lighting.
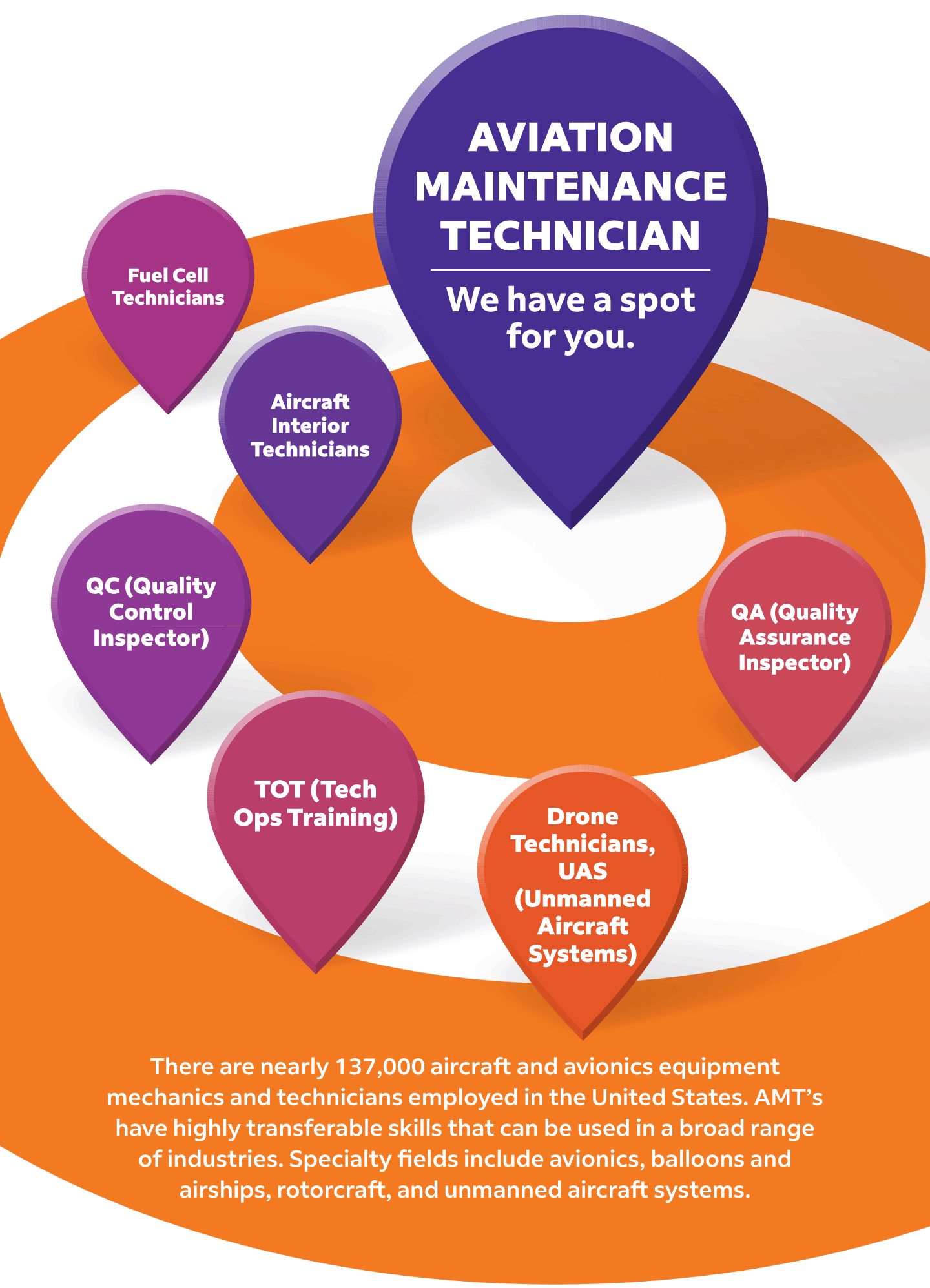
Fuel Cell Technicians
Installs and maintain fuel cell systems and equipment. They design and develop fuel cell systems or processes and test fuel cells.
QC (Quality Control Inspector)
Focuses on the product to find defects that remain after development. QC professionals find these issues in a variety of ways, including software testing and beta or canary testing.
QA (Quality Assurance Inspector)
Primarily focuses on the processes and procedures that improve quality, including training, documentation, monitoring and audits.
Drone Technicians, UAS (Unmanned Aircraft Systems)
Use their knowledge of electronics, machinery, and engineering to repair drones, electronic controls and main boards. Drones are typically synced with smartphones, requiring technicians to be knowledgeable about repairing wireless devices and systems and use various tools and techniques.
Aircraft Interior Technicians
Recovers, fabricates, upholsters, and repairs ceiling, sidewall, cockpit, and door panels; replace and repair passenger, attendant and cockpit seats and overhead bins and galleys; replace and repair flooring, air conditioning ducts. They also replace passenger service units and entertainment equipment such as phones and video monitors.
TOT (Tech Ops Training)
Provides outstanding technical training to engineers and technicians who improve and maintain the reliability of all aircraft types and systems. They are responsible for all facets of training in the preventative maintenance and repair of airplanes to ensure aircraft are airworthy and all technical aspects are documented properly.
© FedEx 2023